PANMONE
Pantoprazole Injection
Pantoprazole Injection is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) used to treat various gastrointestinal conditions by reducing the amount of stomach acid produced. It is an intravenous (IV) formulation of Pantoprazole, which is commonly used when oral medication is not feasible, such as in hospitalized patients.
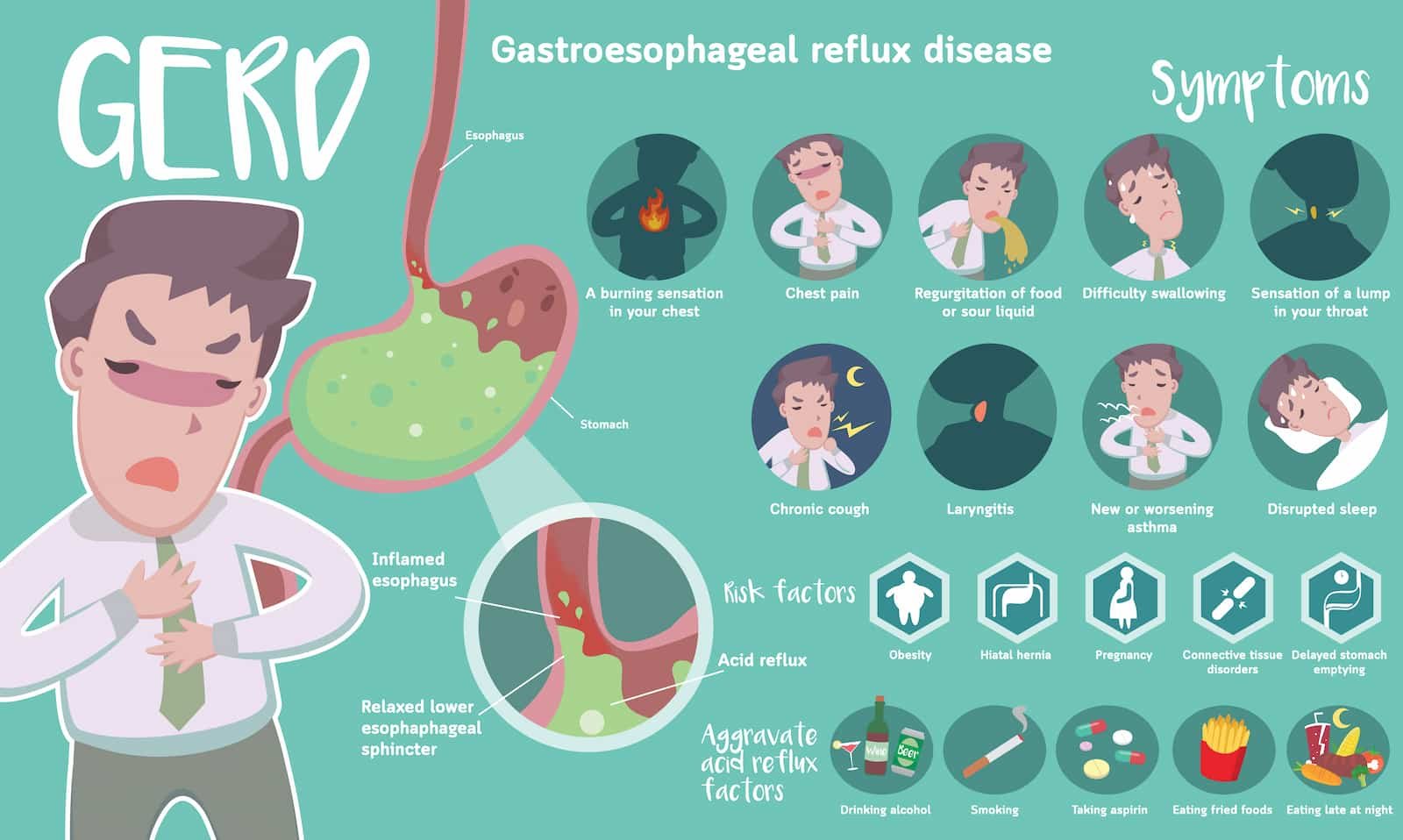
Mechanism of Action
Pantoprazole works by inhibiting the proton pump (H+/K+ ATPase) in the stomach lining. This enzyme is responsible for the final step in the production of gastric acid. By blocking this pump, Pantoprazole reduces the secretion of stomach acid, helping to heal ulcers, prevent acid reflux, and relieve symptoms of conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Indications
Pantoprazole Injection is typically used for the treatment of conditions related to excessive stomach acid production. Some of the primary indications include:
Complicated intra-abdominal infections
(e.g., peritonitis, abscesses)Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
Especially in patients with severe reflux esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus caused by acid) or those who cannot take oral medications.Peptic Ulcer Disease:
To promote the healing of ulcers in the stomach or duodenum.Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome:
A rare condition where the stomach produces too much acid due to tumors in the pancreas or duodenum.Prophylaxis of Gastric Ulcers:
In critically ill patients receiving non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), who are at risk for developing ulcers.Acid-related upper GI bleeding:
As part of the management of active bleeding or to prevent recurrence.
Dosage and Administration
Adults:
The usual dose of Pantoprazole Injection for most conditions is 40 mg intravenously once daily. The injection is typically given as a slow IV infusion over 15 minutes.Short term Use
Pantoprazole is generally used for a short period (e.g., 7-10 days) when patients are unable to take oral medication, particularly in the treatment of GERD or peptic ulcers.Long term Use
If prolonged use is necessary, it should be done with close monitoring by a healthcare provider to prevent complications or side effects.Renal and Hepatic Impairment
In patients with severe liver impairment, the dose may need to be adjusted, but there is no need for dose adjustment in patients with kidney issues.- Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation.
- Headache: A common side effect when using Pantoprazole.
- Injection site reactions: Pain, swelling, or redness at the IV injection site.
- Dizziness or fatigue: Some patients may experience dizziness or feeling tired during treatment.
- Severe gastrointestinal issues: Long-term use may increase the risk of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (C. difficile colitis).
- Kidney problems: Rarely, prolonged use can lead to kidney damage, including acute interstitial nephritis.
- Hypersensitivity: Pantoprazole should not be used in patients with known hypersensitivity to Pantoprazole or any other PPI.
- Long-term use: Prolonged use of Pantoprazole (especially for more than a year) should be monitored, as it may be associated with risks like nutrient deficiencies (e.g., vitamin B12, magnesium) and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Liver Disease: Pantoprazole should be used cautiously in patients with severe liver disease, as it may require dose adjustments.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pantoprazole is classified as Category C for pregnancy, meaning it should only be used if clearly necessary. It is not known if Pantoprazole passes into breast milk, so it should be used cautiously in breastfeeding mothers.
- C. difficile Infection: Prolonged PPI therapy can increase the risk of infections like C. difficile in the colon, leading to diarrhea.
Side Effects
Common side effects include:
